
End Suction Pumps

Wastewater from industries and cities is collected and treated by a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). To put it another way, a WWTP treats water to get rid of waste, grease, floating oils, sand, and any coarse debris that may be present in the water. The treatments get rid of organic and inorganic materials through settling processes, as well as biodegradable organic material that is dissolved in the water. The major aims of treating wastewater can be summarized as follows:
- Reducing water pollution
- Using the waste from treatment procedures to enable a more sustainable use of water resources
Nowadays, much more sophisticated technologies are being introduced by various high-tech industries dealing with wastewater treatment. The technologies deal with effective and cost-efficient methods and supplies to deal with wastewater produced at both domestic and industrial levels.
Pumps
Pumps are one of the major parts of a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP), which helps in the inflow and outflow of water in the plant. In addition to pumping and conveying wastewater, a wastewater pump can also be used to empty sump pumps or dose chemicals to clean bad water. This type of pump is also sometimes called a dirty water pump. The major task of pumps in wastewater plants is pumping and conveying wastewater, as well as emptying submersible pumps and administering chemical doses to treat unclean water.
Challenges with pumps used in Wastewater Treatment Plants
Pumps in a wastewater treatment facility may have a number of problems that could affect the process’s dependability and effectiveness. In this line of work, some of the biggest issues that might occur with pumps are as follows:
Clogging: Pumps used in the wastewater treatment sector frequently get clogged with trash and solid materials. This issue can cause the pump to malfunction or lower its flow rate.
Cavitation: Cavitation is the term used to describe the formation of bubbles when the impeller of a pump produces a vacuum. When these bubbles burst, a pump will experience high-pressure shock waves that could harm the pump and lower its efficiency.
Corrosion: Wastewater treatment facilities commonly employ corrosive chemicals. These could include acids or bases, which can erode pumps and other equipment.
Electrical Issues: Pumps in wastewater treatment plants may malfunction as a result of electrical problems such as power surges and motor breakdowns.
Wear and Tear: Because the fluids handled in the wastewater treatment industry are corrosive and abrasive, pumps in this sector are likely to see high levels of wear and tear.
Hence, there must be complete research conducted prior to the selection of a pump. The current article will provide insightful research on various types of End Suction Pumps that will help you make the right decision in this regard. The article will provide an introduction to End Suction Pumps and enlist some major companies dealing with End Suction Pumps and the specifications of their products. The article will also explain the features that help to recognize the standout points of technology.
End Suction Pump
A popular centrifugal pump used for moving liquids from one place to another is the end suction pump. The pump’s design places the connections for its inflow and outflow at the same end of the pump casing. Because it may be installed vertically or horizontally and requires less piping, this design makes the pump simple to maintain and operate.
The pump functions by utilizing a high-speed rotating impeller to transform mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. A low-pressure area forms in the center of the impeller. As a result, a centrifugal force is generated by the impeller’s rotation, which transports wastewater to the other end of the blades. The liquid enters this low-pressure region through the intake connection and is forced out through the outlet connection.
For most daily pumping applications, end-suction pumps are the most economical option. Numerous manufacturers produce end-suction pumps in a variety of construction materials, both off-the-shelf and custom-engineered equipment.
Common Applications
Some common applications of end suction pumps are given below:
- Refrigerators
- Wastewater Treatment
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Agricultural Irrigation System
- Sprinklers
- Food and Drink Manufacturing Industries
- Firefighting Systems
- Cooling Towers
- Water Pumping Systems
Advantages
The End Suction Pump upholds the following major advantages:
- These pumps have low installation costs compared to other technologies
- Despite being low-cost, the efficiency and working capacity of these pumps are very high.
- These are easy to install due to their simple design.
- The design of the pump also demands very little maintenance and is also simple to operate.
- These pumps don’t need extra space for installation.
- It allows easy interchange of various parts of pumps and provides quick troubleshooting.
- These pumps also make noise of considerably and comparatively low decibels.
- A considerable range of sizes and designs are available in this category. It will allow for better application in approximately each field of life.
Disadvantages
There are the following major disadvantages of End Suction Pump;
- Although these types of pumps have a wide variety of applications, there are a number of uses in which they don’t fit better.
- The pump also needs a complete priming before being operational.
- The working of the pump is also disturbed when it gets filled with air (experience cavitation).
- These pumps are not very efficient for the transportation of highly viscous materials.
- These pumps consume high power as compared to other technologies for the transportation of large amounts of liquid with a high flow rate.
- In the case of transportation of corrosive liquids, these pumps are not very efficient as the impellers can be corroded.
Product Selection Criteria
The best products of End Suction Pumps are being selected based on the following criteria:
Flow Rate: Pump flow rate is one of the important factors when selecting an end suction pump for wastewater treatment. Flow rate is actually how much water the pump can move in a given period of time. Using the right flowmeter to measure flow rates accurately is essential to making sure fluid control operations are efficient, safe, and economical. Thus, the flow rate also helps to check the following three parameters;
- Quality Control
- Health and Safety
- Cost-effectiveness
Hence, while selecting an end suction pump, analyzing the flow rate of the pump was a primary focus.
Impeller: Impeller carries out the main task of transforming the motor’s mechanical energy into kinetic energy. This energy increases the fluid’s pressure and flow rate. Higher flow rates are achieved when an impeller with a greater diameter can handle more fluid. However, the rotational energy required is greater, leading to increased energy consumption.
Hence, the pump selection was done by considering liquids with high viscosity and solid debris. It was also considered that as some types of wastewater with high organic content produce different gases such as methane, sulfur dioxide, etc., the Vortex impeller was also selected for such purpose to tackle the transport of these gases.
Temperature and pressure: Temperature and pressure can affect the efficiency of pumps as, at a certain level, the material of pumps starts to corrode. The normal temperature of wastewater is around 60 – 95℉, while pressure depends on the source. Hence, the pumps were selected by considering that they can operate at maximum as well as minimum possible temperatures and pressures.
12 best manufacturer companies of End Suction Pumps
Some well-known companies dealing with End Suction Pumps are as follows:
- Grundfos
- Xylem
- Sulzer
- KSB
- Armstrong Field Technology
- Pentair Aurora
- Wilo
- Flowserve
- Ebara Cooperation
- Teikoku USA
- Dickow Pump Co.
- Kaikuan
The current section will provide insight into various models of End Suction Pumps by the world’s best companies. The section will focus on residential, commercial, and industrial wastewater treatment plants and well-suited End Suction Pumps for those plants.
Grundfos
Grundfos is the world’s largest company investing in the pump manufacturing industry. The industry was established in 1945 in Denmark. Currently, more than 19,000 people are working in this space. The company is a premium supplier of pumps, as it produces approximately 17 million pumps each year and upholds nearly 50% of global revenue in the industry of circulating pumps. The simple agenda of the company revolves around five pillars, i.e., quality, innovation, design, manufacturing excellence, and energy efficiency.
Grundfos produces 10 main types of pumps, including End Suction Pumps with further categories.
Specifications
End Suction Close-coupled single-stage
Model: NBG 125-100-250/275 VBAF2CESBQQESY1
Head: 31.15 m
Pump Speed: 2960 RPM
Rated Flow: 133.9 m³/h
Actual Impeller Diameter: 275 mm
Nominal Impeller Diameter: 250
Liquid temperature range: -25 – 120 °C
Pressure: 16 bar
Mains Frequency: 50 Hz
IE Efficiency: IE3 93.7%
Type of impeller: SuperVortex
Max. Particle: 25 mm
Shaft seal arrangement: Single
Shaft diameter: 42 mm
Code for shaft seal: BQQE
Curve tolerance: ISO9906:2012 3B
Pump Version: A
Bearing design: Standard
Net Weight: 387 kg
Gross Weight: 412 kg
Shipping Volume: 0.707 m³
Materials
Pump Housing: Cast Iron
EN-GJL-250
ASTM Class 35
Wear Ring: Brass
Impeller: Cast Iron
EN-GJL-200
ASTM Class 30
Internal Pump House Coating: CED
Material Code: C
Code for Rubber: E
Shaft: Stainless Steel
EN 1.4401
AISI 316
Applications:
- Commercial wastewater
- Machining
- Process liquids transfer
- Industrial process water treatment
- Industrial cleaning process
- Industrial water supply and transfer
- Industrial wastewater treatment and reuse
- Wastewater transport
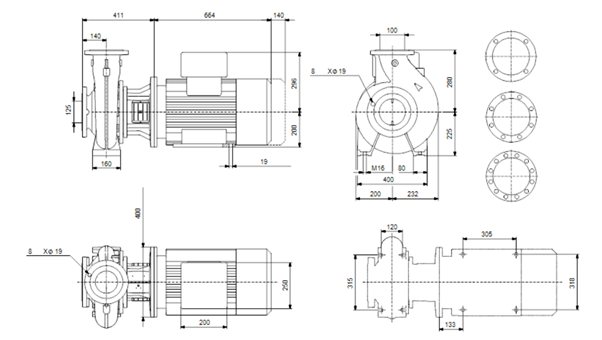 Figure 1. Dimensional Drawing of End Suction Close-coupled single-stage: NBG 125-100-250/275 VBAF2CESBQQESY1
Figure 1. Dimensional Drawing of End Suction Close-coupled single-stage: NBG 125-100-250/275 VBAF2CESBQQESY1
End Suction Long Coupled Single Stage
Model: NK 350-350/416-382 AA1F1SBESBQQEYW3
Head: 34.45 m
Pump Speed: 1485 RPM
Rated Flow: 1917 m³/h
Actual Impeller Diameter: 399 mm
Nominal Impeller Diameter: 350 mm
Liquid temperature range: -25 – 120 °C
Pressure: 10 bar
Mains Frequency: 50 Hz
IE Efficiency: IE3 96%
Motor Type: 315L
Rated power – P2: 200 kW
Motor Efficiency at Full Load: 96% – 96%
Max. Particle: 25 mm
Shaft diameter: 60 mm
Mechanical Seal Type: Single
Code for shaft seal: BQQE
Curve tolerance: ISO9906:2012 2B
Pump Version: A1
Bearing design: Standard
Net Weight: 2270 kg
Gross Weight: 2430 kg
Shipping Volume: 5.6 m³
Materials
Pump Housing: DUCTILE IRON
EN 1563 EN-GJS-500-7
ASTM 70-50-05
Impeller: Stainless steel
EN 1.4308
ASTM A351 CF8
Internal Pump House Coating: Painting
Material Code: SB
Code for Rubber: E
Shaft: Steel
EN 1.0503/1.4301
AISI 1045/304
Applications:
Water Treatment Fertigation, Chemigation & Dosing
Irrigation
Desalination
Community water supply
Water distribution
Wastewater treatment
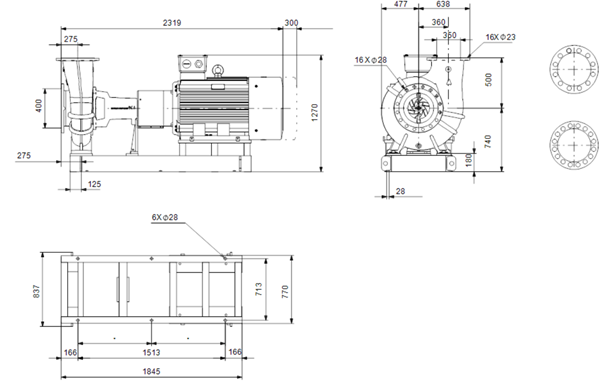 Figure 2. Dimensional Drawing of End Suction Long coupled single-stage: NK 350-350/416-382 AA1F1SBESBQQEYW3
Figure 2. Dimensional Drawing of End Suction Long coupled single-stage: NK 350-350/416-382 AA1F1SBESBQQEYW3
Xylem
Xylem is a multinational manufacturer of sensors, pumps, monitoring, and control equipment intended especially for use in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment applications. Products from Xylem’s international brands have been sold in more than 150 countries, catering to the water market for many years. Xylem provides cutting-edge water technology solutions for the entire water cycle in a world where challenges are only getting bigger.
Xylem can be considered the second-best option to purchase End Suction Pump. The company is well known for its innovative technologies and reduced life cycle cost of products.
Xylem’s manifesto is;
“Xylem serves a variety of industries, such as public utilities, agriculture, building, construction, environmental, food and beverage, government agencies, and industrial and commercial building services. With extensive application knowledge in the water sector, we concentrate on developing extremely energy-efficient water solutions that lower lifecycle costs, benefit users and the communities where they operate, and improve the environment.”
Goulds Water Technology e-NSC – Series
Rated Flow: up to 1800 m³/h
Head: up to 160 m
Power Supply: three-phase 50 and 60 Hz
Power: 0.25 – 355 kw
Maximum Operating Pressure: 16 bar
Temperature Of Pumped Liquid: -25°C – +140°C
Motor Efficiency: IE3 or higher-rated motors
F (155°C) insulation class
Protection grade: IP55 – 50Hz and 60Hz voltages
A wide range of motor options
Material: Stainless Steel
Cast Iron
Applications:
- Municipal Water and Wastewater
- Water transfer and distribution
- Water intake and monitoring solutions for clean water
- Municipal Sewage Handling & Waste Treatment
- HVAC Heating
- HVAC Cooling
- Mine Water Boosting & Transport – Pumps, Monitoring and Controls
- Offshore Oil Platform Water Management
 Figure 3. Goulds Water Technology e-NSC – Series
Figure 3. Goulds Water Technology e-NSC – Series
Bell & Gossett Series e-1535 Close-Coupled Small End Suction Pumps
Model: e3509T
Pump Size: 1.25AAC
Pump Construction: Cast Iron-BF (Brz Fitted)
Pump Class: Centrifugal
Pump Mounting: Foot-Mounted
Pump Connection Size: 1-1/2″ x 1-1/4″
Pump Connection: Threaded
Flanges Included: N/A
Motor HP: 1/2 HP
Motor RPM: 1725 RPM
Motor Voltage: 208-230/460V
Motor Phase: 3 Ph
Motor Hertz: 60 Hz
Shaft Size: 5/8″
Impeller Size: 5″
Working Pressure: 175 psi
Max Temp: 250℉
Weight: 55.00 kg
Material:
Volute: Cast Iron ASTM #A159
Impeller: ASTM #B584
Volute Gasket: Cellu-Fiber
Shaft: Stainless Steel
Bracket: Cast Iron – ASTM #A48
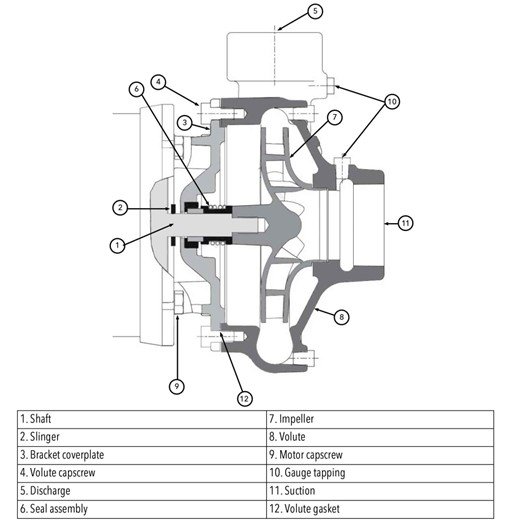 Figure 4. Cross-Sectional View of Bell & Gossett Series e-1535 Close-Coupled Small End Suction Pumps
Figure 4. Cross-Sectional View of Bell & Gossett Series e-1535 Close-Coupled Small End Suction Pumps