Maximizing Efficiency with Sequencing Batch Reactors: Design and Operation Tips

Maximizing Efficiency with Sequencing Batch Reactors: Design and Operation Tips
Introduction
Welcome to the world of sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), where efficiency meets innovation in wastewater treatment! If you’ve ever wondered how municipalities and industries tackle the Herculean task of cleaning up our water, you’re in for a treat. SBRs are like the Swiss Army knives of the wastewater management landscape compact, versatile, and ready to tackle various challenges with style.
In an era where water resource recovery is more crucial than ever, understanding the intricacies of SBR systems can give you a leg up. These systems not only handle biological treatment but also excel in nutrient removal, making them a popular choice for modern sewage treatment plants. Think of SBRs as the superheroes of wastewater recycling, swooping in to save the day by converting waste into clean water that meets stringent effluent quality standards.
But what makes these batch process reactors so special? For starters, they offer remarkable flexibility. SBRs can adapt to varying flow rates and loads a feature that traditional methods often struggle with. This adaptability is essential for effective wastewater management, especially in fluctuating conditions found in municipal settings or industrial applications.
Throughout this blog post, we’ll dive into design considerations, operational tips, and sustainable practices that will help you maximize efficiency with sequencing batch reactors. Whether you’re an engineer looking to optimize your system or a municipal operator aiming to meet environmental regulations, we’ve got insights that will help you navigate this complex yet fascinating field.
Understanding Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBR)
Welcome to the world of sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), where wastewater treatment meets efficiency in a delightful dance of biological processes. Think of SBRs as the multitaskers of the wastewater management realm, combining various stages of treatment into one compact package.
Definition of Sequencing Batch Reactors
At its core, an SBR is a type of batch process reactor designed for the treatment of wastewater. These systems operate by filling a single tank with sewage, treating it, and then discharging it in a series of steps. It’s like cooking a gourmet meal you gather your ingredients (wastewater), mix them together (biological treatment), and serve them up (effluent quality) all in one pot!
Overview of the Sequencing Batch Process
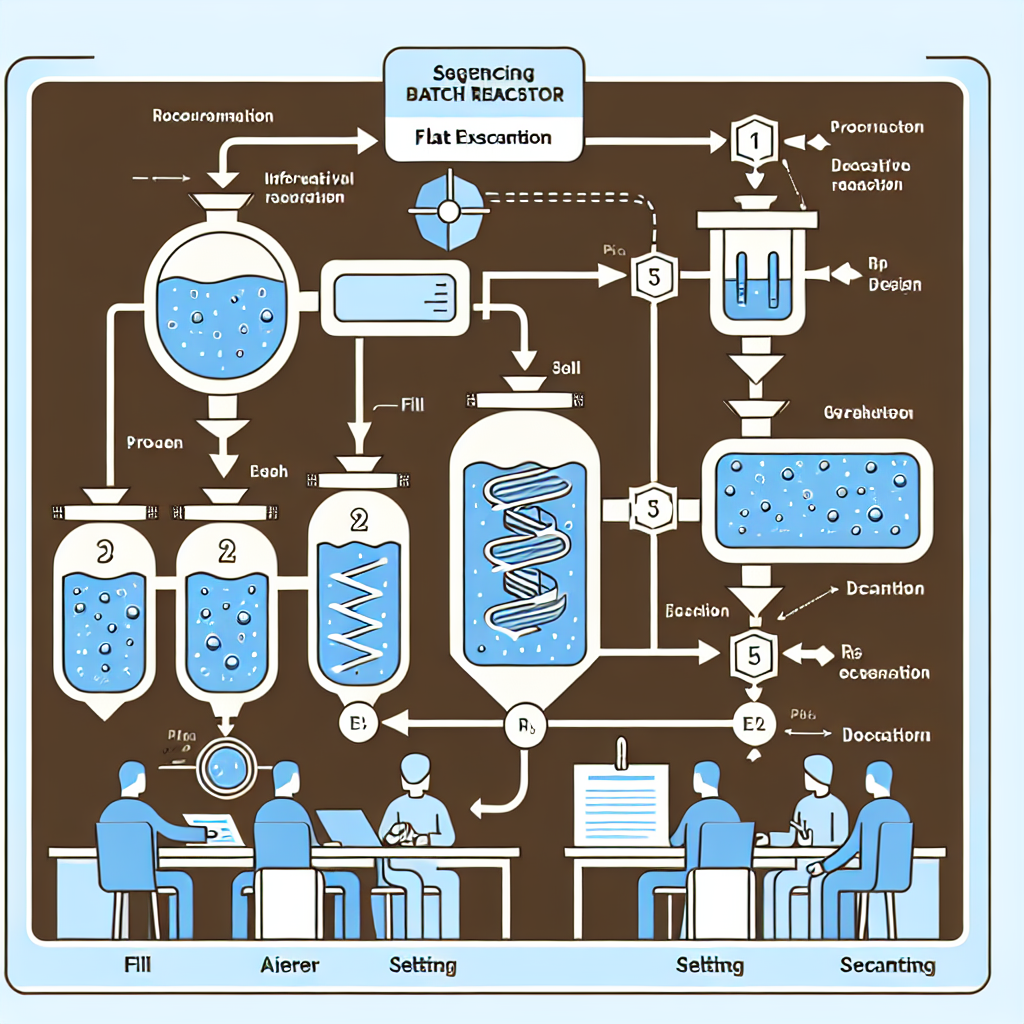
The sequencing batch process involves several key phases:
- Fill: The tank fills with influent wastewater.
- Aeration: Oxygen is introduced to support microbial growth and nutrient removal.
- Settling: Solids settle at the bottom, separating from treated water.
- Decanting: The clarified effluent is drawn off for discharge or further treatment.
- Idle: The tank may remain idle while waiting for the next cycle.
Comparison with Traditional Wastewater Treatment Methods
SBRs are often compared to traditional continuous flow systems like activated sludge processes. Here’s how they stack up:
| Feature | SBR Systems | Traditional Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment Phases | Cyclic (fill, aerate, settle, decant) | Continuous flow through multiple tanks |
| Nutrient Removal Efficiency | High | Moderate to High |
| Footprint Size | Compact | Larger due to multiple tanks |
| Operational Flexibility | Easily adjustable cycles for varying loads | Lesser flexibility; more complex adjustments needed |
If you’re still wondering why SBRs are gaining traction in modern wastewater treatment facilities, consider this: they combine simplicity with advanced biological nutrient removal (BNR) techniques making them a go-to choice for both municipal and industrial applications. Plus, they’re energy efficient! Who doesn’t love saving on energy bills while keeping our precious water resources clean?
This understanding sets the stage for diving deeper into design considerations that can further enhance the performance of your SBR systems.
Design Considerations for SBR Systems
When it comes to designing sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), think of it like assembling a superhero team. Each component needs to work in harmony to tackle the challenges of wastewater treatment. Here are some essential design considerations that can make or break your SBR system:
-
Key Design Parameters for Effective Operation
The foundation of any successful SBR lies in its design parameters. You need to consider:
- Hydraulic retention time (HRT): This is crucial for ensuring enough time for biological processes.
- Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS): Balancing this helps optimize the activated sludge process.
- Cyclic operation schedules: Fine-tuning these can enhance nutrient removal and overall efficiency.
-
Sizing of Aeration Tanks and Reactors
Sizing is not just about fitting everything into a box; it’s about ensuring that your aeration tanks and reactors can handle peak loads without breaking a sweat. Over-sizing can lead to inefficiencies, while under-sizing can compromise effluent quality. Aim for a Goldilocks approach: not too big, not too small, but just right!
-
Integration with Existing Wastewater Management Systems
Your new SBR system should play nicely with current infrastructure. Consider factors such as:
- Flow rates: Ensure the new system can handle fluctuations in inflow.
- Compatibility: Check if existing components like pumps and tanks are suitable for your new design.
- Regulatory compliance: Make sure your design meets local wastewater effluent standards to avoid any nasty surprises down the line.
-
Compact Wastewater Systems for Urban Settings
If you’re working in an urban environment, space is likely at a premium. Compact wastewater systems are the way to go! These systems not only save space but also reduce construction costs and make maintenance easier. Think of them as the tiny homes of wastewater treatment efficient and stylish!
Takeaway: Designing an effective SBR system requires careful consideration of parameters, sizing, integration, and compactness especially in urban settings. Get these right, and you’ll be well on your way to achieving optimal performance!
The world of wastewater management is evolving rapidly with innovative technologies emerging every day. Stay tuned as we explore operational tips next that will help you maximize efficiency even further!
Operational Tips for Maximizing Efficiency
When it comes to sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), efficiency is the name of the game. These systems can be like a well-oiled machine, but only if you know how to fine-tune them. Here are some operational tips that will help you maximize efficiency and boost your wastewater treatment game.
Controlled Aeration Cycles in Reactors
The heart of any SBR system is its aeration tank, where the magic of biological treatment happens. Implementing controlled aeration cycles can significantly improve the performance of your SBR. By adjusting the duration and intensity of aeration based on real-time data, you can optimize oxygen transfer rates and enhance microbial activity.
Key Point: Utilizing sensors and automated controls for aeration can lead to a 15-20% reduction in energy consumption while maintaining effluent quality.
Nutrient Removal Strategies in SBRs
Nutrient removal is crucial for meeting wastewater effluent standards. To effectively manage nutrient loads, consider integrating advanced nutrient removal strategies such as:
- Intermittent Aeration Process: This method alternates between aerobic and anoxic phases, allowing for optimal nitrogen removal.
- Cyclic Activated Sludge System Optimization: Tailor your cycles based on influent characteristics to enhance biological nutrient removal (BNR).
- Aerobic Digestion: Implement aerobic digestion processes within your SBR to minimize sludge production while maximizing nutrient uptake.
Aerobic Digestion in SBRs for Waste Minimization
Aerobic digestion isn’t just a buzzword it’s a game changer! By incorporating aerobic digestion into your SBR operations, you can significantly reduce solid waste generation. This process not only stabilizes sludge but also enhances biogas production, making it a win-win for both efficiency and sustainability.
Cyclic Activated Sludge System Optimization Techniques
The cyclic activated sludge system (CASS) approach allows for flexibility in treatment processes. To optimize this technique:
- Adjust Cycle Times: Experiment with different cycle lengths to find the sweet spot that suits your specific wastewater characteristics.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Use advanced monitoring systems to track performance metrics continuously. This data-driven approach enables quick adjustments that keep your system running smoothly.
- Operator Training: Invest in training programs for operators to ensure they are familiar with control strategies and troubleshooting techniques specific to SBR systems.
The operational success of your sequencing batch reactors hinges on these strategies. By implementing controlled aeration cycles, focusing on nutrient removal, leveraging aerobic digestion, and optimizing cyclic processes, you’re not just treating wastewater you’re transforming it into a resource!
Remember: Every tweak you make today could lead to significant gains tomorrow. So roll up those sleeves and get ready to dive into the world of efficient wastewater management!
Ensuring High Effluent Quality Standards
When it comes to sequencing batch reactors, ensuring high effluent quality is not just a checkbox on a list it’s the very essence of effective wastewater treatment. Think of it as the difference between serving a gourmet meal and slapping together leftovers. Your end product reflects your process, and in the world of wastewater management, that means adhering to stringent effluent quality standards.
Understanding Wastewater Effluent Standards
First things first: what are these magical standards? Essentially, they are regulatory benchmarks that dictate how clean your treated water must be before it’s released back into the environment or reused. These standards vary by region but typically focus on parameters such as:
- BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand)
- TSS (Total Suspended Solids)
- Nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus
- Pathogen levels
Monitoring and Control of Effluent Quality Parameters
Next up, monitoring is essential. You wouldn’t drive a car without checking the fuel gauge, right? In SBR systems, regular monitoring of effluent quality parameters ensures you stay within compliance limits. Implementing automated sensors can streamline this process, providing real-time data on:
- Water clarity and turbidity
- Dissolved oxygen levels
- Nutrient concentrations
Key Takeaway: Regular monitoring not only helps maintain compliance with wastewater effluent standards but also allows for quick adjustments to treatment processes when necessary.
Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR) Practices in SBRs
If you’re looking to up your game in nutrient removal, consider integrating Biological Nutrient Removal (BNR) practices into your sequencing batch process. BNR can effectively reduce nitrogen and phosphorus levels through:
- Aerobic digestion techniques that enhance microbial activity
- Cyclic aeration processes that optimize nutrient uptake
- Strategic timing of anaerobic phases to facilitate nutrient release and uptake during aerobic phases
This approach not only meets environmental regulations but also contributes to sustainable water management practices by minimizing nutrient overloads in receiving waters.
A Common Misconception: Size Matters!
A common misconception is that bigger reactors always mean better effluent quality. Not true! It’s all about how well you manage your SBR systems. Overloading an SBR can lead to poor treatment performance regardless of its size. It’s crucial to balance the load with reactor capacity while maintaining optimal operational conditions.
In summary: By understanding wastewater effluent standards, implementing robust monitoring systems, and adopting effective BNR practices, you can ensure that your sequencing batch reactors deliver high-quality effluent consistently. This not only keeps regulatory bodies happy but also promotes a healthier environment for everyone.
Ready to take your SBR game to the next level? Dive deeper into operational strategies or explore innovative technologies that enhance efficiency!
Sustainable Practices in Wastewater Treatment Using SBRs
When it comes to wastewater treatment, sustainability is not just a buzzword it’s a necessity! Enter sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), the unsung heroes of modern wastewater management. These systems are not only efficient but also pave the way for eco-friendly practices that can make your treatment plant the envy of the neighborhood.
Energy-Efficient Wastewater Treatment Solutions
One of the most significant benefits of SBRs is their ability to optimize energy consumption. By utilizing controlled aeration cycles, these reactors can significantly reduce energy usage compared to traditional continuous flow systems. Imagine being able to run your plant like a smart thermostat only using energy when it’s truly needed!
Innovative Wastewater Technologies for Sustainable Management
The world of wastewater treatment is evolving faster than a cat meme goes viral! Advanced technologies integrated with SBR systems are enhancing biological treatment processes and improving overall efficiency. For example, integrating sensors and automation can help monitor real-time data, allowing operators to adjust parameters on-the-fly, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with stringent wastewater effluent standards.
Adaptive Reuse of Water Resources in Industrial Settings
Picture this: an industrial facility that treats its own wastewater on-site using SBR technology, then reuses that water for cooling processes or even irrigation. This is not just futuristic thinking; it’s happening now! By implementing innovative strategies, industries can achieve significant reductions in freshwater intake while also minimizing their environmental footprint.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing sustainable practices in SBR operations not only enhances environmental performance but also leads to cost savings. This dual benefit makes it an attractive option for municipalities and industries alike!
In conclusion, embracing sustainable practices in wastewater treatment using SBRs isn’t just about following trends; it’s about leading the charge toward better water resource management. As we continue to innovate and adapt our approaches, SBR systems will play a crucial role in shaping the future of water purification systems.
The Future of Wastewater Treatment with SBR Technologies
The landscape of wastewater treatment is changing faster than a cat meme goes viral! With the rise of sequencing batch reactors (SBR), we’re seeing a transformation that’s not just about cleaning up our act but doing it in a way that’s smarter, greener, and more efficient.
As we look to the future, several key trends are emerging in the realm of engineered wastewater systems design:
- Integration of Advanced Technologies: The incorporation of IoT and AI into SBR systems is revolutionizing how we monitor and manage wastewater. Imagine real-time data analytics predicting maintenance needs or optimizing aeration cycles it’s like having a crystal ball for your treatment plant!
- Sustainable Practices: The push for sustainability is stronger than ever. SBRs are being designed with energy efficiency in mind, utilizing renewable energy sources and innovative technologies to reduce their carbon footprint. Think solar panels on your wastewater facility it’s not just sci-fi anymore!
- Nutrient Recovery: With stricter regulations on nutrient removal, SBRs are stepping up to the plate. They’re not just treating wastewater; they’re also recovering valuable resources like nitrogen and phosphorus, turning potential pollutants into profit.
The role of SBRs in municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) is also expanding. These compact systems are ideal for urban settings where space is at a premium. They can handle varying flow rates and loads, making them perfect for cities experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations.
Did you know? SBRs can achieve effluent quality standards that meet or exceed those required by regulatory agencies, making them a go-to solution for both municipal and industrial applications.
Moreover, as industries embrace the concept of circular economy principles, SBR technologies will play a pivotal role in industrial wastewater solutions. By enabling efficient recycling and reuse of water resources, these systems help businesses minimize waste while maximizing operational efficiency it’s like finding money in your couch cushions but better!
According to recent studies, SBRs can improve overall system performance by up to 30% compared to traditional activated sludge processes.
However, there are still common misconceptions about SBR technologies that need addressing. One major myth is that they require extensive operator training due to their complexity. In reality, many modern SBR systems come equipped with user-friendly interfaces that simplify operation and monitoring.
In summary, as we move toward more innovative wastewater technologies, the future looks bright for sequencing batch reactors. They represent not just a shift in technology but a shift in mindset towards sustainable water management practices that prioritize efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Tangible Takeaway: If you’re involved in designing or operating wastewater facilities, consider how integrating SBR technologies can enhance your processes today while preparing you for tomorrow’s challenges.
Conclusion
article blockquote,article ol li,article p,article ul li{font-family:inherit;font-size:18px}.featuredimage{height:300px;overflow:hidden;position:relative;margin-top:20px;margin-bottom:20px}.featuredimage img{width:100%;height:100%;top:50%;left:50%;object-fit:cover;position:absolute;transform:translate(-50%,-50%)}article p{line-height:30px}article ol li,article ul li{line-height:30px;margin-bottom:15px}article blockquote{border-left:4px solid #ccc;font-style:italic;background-color:#f8f9fa;padding:20px;border-radius:5px;margin:15px 10px}article div.info-box{background-color:#fff9db;padding:20px;border-radius:5px;margin:15px 0;border:1px solid #efe496}article table{margin:15px 0;padding:10px;border:1px solid #ccc}article div.info-box p{margin-bottom:0;margin-top:0}article span.highlight{background-color:#f8f9fb;padding:2px 5px;border-radius:5px}article div.info-box span.highlight{background:0 0!important;padding:0;border-radius:0}article img{max-width:100%;margin:20px 0}